Gelato VRF
Mechanism: Uses Drand, a decentralized source for random numbers.
Benefits: Provides genuine, verifiable random values for blockchain applications.
Applications of Gelato VRF
Gaming and Gambling: For fair outcomes in online games and decentralized gambling.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Random selections for lotteries in DeFi protocols.
NFT Generation: Random trait generation for unique digital assets.
Protocol Decision Making: Randomized selections for validators or jurors.
Steps to Set Up Gelato VRF
Set Up Development Environment: Install either Foundry or Hardhat.
Install Gelato VRF Contracts: Use specific commands for Hardhat or Foundry.
Inherit
GelatoVRFConsumerBaseContract: Incorporate it into your contract.Request Randomness: Call
_requestRandomness()function.Implement Callback Function: Define how your contract handles the randomness response.
Include
dedicated msg.sender: Essential for contract security and function.
Quick Start
Step 1: Set Up Your Development Environment
Make sure you have Hardhat or Foundry ready for use.
Step 2: Install Gelato VRF Contracts
For Hardhat, clone the repository and set up the environment. For Foundry, use the forge install command.
Step 3: Inherit GelatoVRFConsumerBase Contract
Create a contract that inherits from GelatoVRFConsumerBase.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.18;
import {GelatoVRFConsumerBase} from "./GelatoVRFConsumerBase.sol";
contract YourContract is GelatoVRFConsumerBase {
// Your contract's code
}
Step 4: Request Randomness
To request randomness, call the _requestRandomness() function. You should protect the call since it will take from your 1Balance. The data argument will be passed back to you by the W3F.
function requestRandomness(bytes memory data) external {
require(msg.sender == ...);
uint64 requestId = _requestRandomness(data);
}
Step 5: Implement Callback Function
function _fulfillRandomness(
bytes32 randomness,
uint64 requestId,
bytes memory data,
) internal override {
}
}
Step 6: Include Dedicated msg.sender
When you're ready to deploy your Gelato VRF-compatible contract, an important step is to include the dedicated msg.sender as a constructor parameter. This ensures that your contract is set up to work with the correct operator for fulfilling the randomness requests.. It's crucial for ensuring that only authorized requests are processed.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.18;
import {GelatoVRFConsumerBase} from "./GelatoVRFConsumerBase.sol";
contract YourContract is GelatoVRFConsumerBase {
constructor(address operator)
GelatoVRFConsumerBase(operator) {
// Additional initializations
}
// The rest of your contract code
}
Task Creation
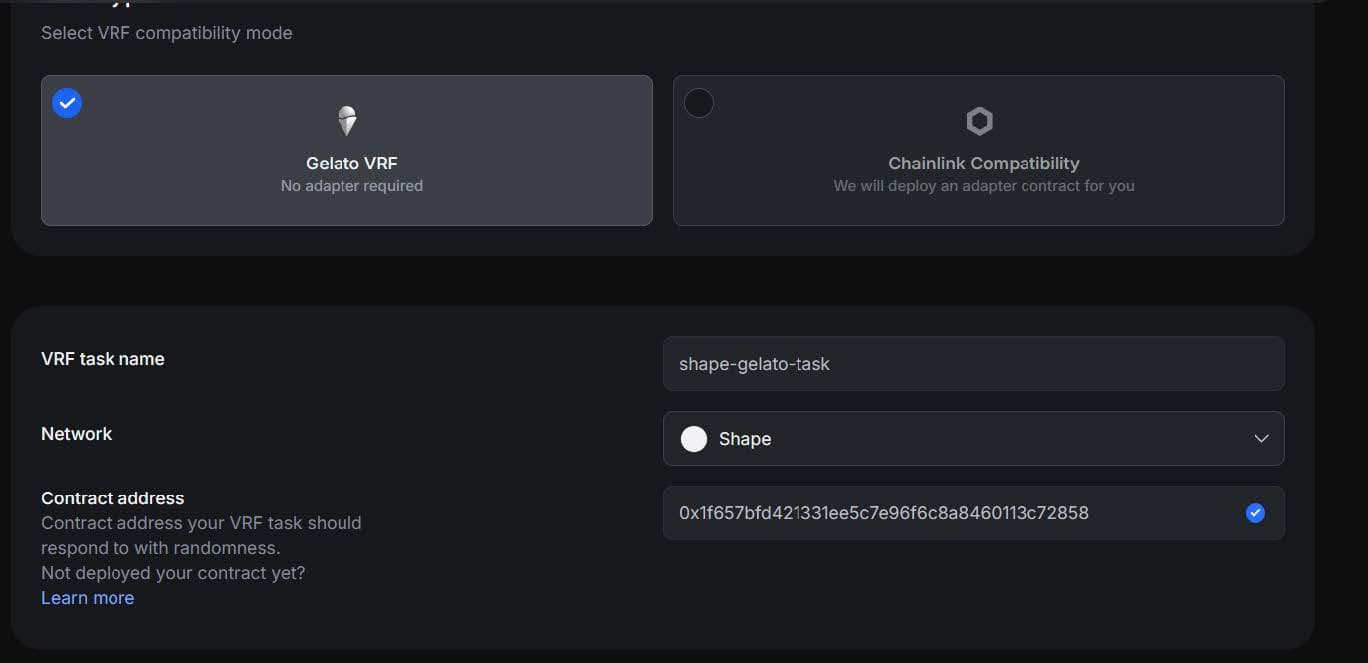
Upon deploying your contract, you will need to create a Gelato Task. This can be done via the Gelato UI. Next, you will be prompted to provide the address of the Request Contract to which the Gelato nodes should respond. Enter the address of your contract, and once all details have been correctly entered, proceed with launching your Gelato VRF instance.
Now everytime you call the _requestRandomness() function, the Gelato nodes will respond with a random number that you can use in your contract.
For more detailed information, refer to the Gelato VRF documentation.